Vascular & Wound Care
Critical Limb Ischemia and chronic wounds
Most common cause of non healing wounds are peripheral arterial occlusive (PAD) And Diabetic Microangiopathy Risk factors associated with the development of PAD include individuals aged 65 years and older, Nicotine use, Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and family history of cardiovascular disease.
Open surgical techniques to remove the blockage (bypass) endovascular treatment(balloon angioplasty) is mainstay of revascularisation:, While the mechanism of action has not been Patients who have failed or who are no longer candidates for these therapies, 20% will die and 50–90% a leg amputation in 6 months.
Research focused on the use of autologous cell therapy has shown promise and has led to several clinical studies where concentrated autologous bone marrow cells have been used as an Angiogenic treatment in patients who are not candidates of open or endovascular procedure
How it works
The mechanism of action is postulated is that the improvements shown in perfusion and concomitantly in quality of life and walking capacity result from the effect of bone marrow cells on the small collateral vessels. The expansion of these vessels is the most important physiological repair mechanism in peripheral artery disease
How it is done
As a day care procedure 240 ml of Bone marrow OR 100 ml of fat is aspirated and processed for stem cells isolation. stem cells processed as per GMP are injected either into
1. Intralesional into the wound and around margins
2. Intrarterial administration of via Angiography
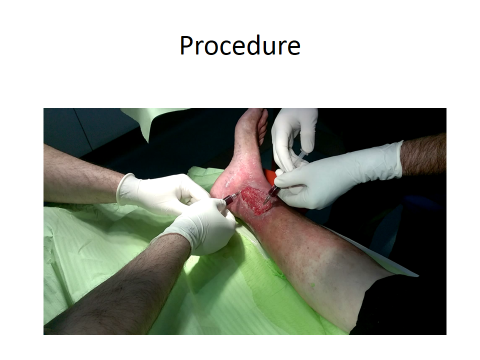
Application of stem cells into and around margins of wound

Intrarterial administration of stem cells via Angiography
What to expect
- Ankle-brachial index was significantly improved at rest from 0.66 to 0.80, after stress from 0.64 to 0.76
- 90 % of patients reported amelioration of rest pain and pain free walking time by 24-week
- Pain-free walking distance increased from average of 150 m to 550m
- Angiography evidence of collateral vessel formation observed in 70 % of the patients
- Only 5 % patients needed amputation.
