Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, also called juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that frequently presents itself from infancy to the late 30s. The fundamental cause of type 1 diabetes is the absence of pancreatic beta islet cell (beta cell). For unknown reasons, the immune system sometimes launches an attack against the body’s own insulin-producing beta cells and destroys them.
Intravenous infusion would exert immunomodulatory effects including protection against autoimmune diabetes and facilitate regeneration of pancreatic beta cells probably by curtailing autoimmune responses and recruitment of progenitors of insulin-producing beta cells.
Procedure
Fat and bone marrow is harvested and processed (see technique). Allogenic umbilical cord MScs may be needed in few cases.
Infusion into the feeding artery of pancreatic tail will facilitate regeneration of beta cells responsible for production of insulin
Results
In new onset type 1 approximately 60 % were able to discontinue insulin injections for at least three month post therapy, with 40 % being able to remain off insulin for over 10 months. The therapy improved C-peptide, insulin utilization, and HbA1c at 12 months after the transfusion
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder with the ultimate pathology being a failure of the pancreas to produce a sufficient amount of insulin to appropriately regulate glucose levels in the body.
Procedure
Fat and bone marrow is harvested and processed (see technique).
The use of cell therapy to date for treating T2D has focused on a protocol of delivery of concentrated marrow cells into the feeding artery of Pancreatic tail .
We have developed a new protocol wherein which we inject also
- Into the wall of the duodenum via an endoscopic procedure to Repair damaged cells of the foregut
- into the portal vein via a catheter Repairing damaged portal vein nerves
Results
- Overall 80 % patients show significant response over 2 years
- Fasting blood sugar from 8.5 to 9.5 mmol/L maintained to near diabetic goal of 7 in 80 % of patients.
- HbA1c decline significantly by one year in 80 % of patients. (Average baseline values of from 8- 9.2 to 7.0 -7.5)
- 30% achieved HbA1c values of <7%.
- Fasting C- peptide level improve significantly in 70 % (0.6 -14 to 1.1to 2.2)
- 50% of patients needed 50 percent less requirement of insulin within 6 months.
- 20 % patients achieve reduction in insulin requirement by 75% as compared to baseline
- 10 % patients are able to discontinue insulin completely for 2years
- Insulin level basal mu/ml improved from mean of 16 to 13.5, and after meal from mean of 20 to 32.
- Triglycerides levels slowly reduce over time but at times fluctuate as well
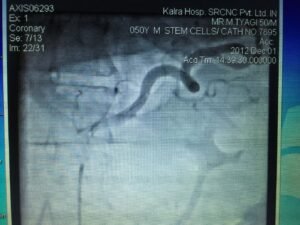
Angiogram showing localising of feeding artery of pancreas before administration of cells
